Imagine a growing manufacturing company overwhelmed by rising customer demand. Inventory details are scattered across multiple files, departments operate in silos leading to delayed orders, and financial reports take weeks to finalize. The leadership team knows improvement is essential but lacks a clear direction. This is where ERP implementation services can bring transformative results.
According to a 2024 report by Grand View Research, the global ERP software market is projected to reach USD 123.41 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 10.7% due to rising demand for integrated business solutions. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a powerful system that connects and automates key business functions within a single platform. However, its true potential is unlocked only through effective implementation.
A strategic ERP rollout not only enhances efficiency but also drives innovation and positions the business for scalable, long-term growth. In this article, we will discuss ERP planning, deployment, and integration to help you understand and optimize your implementation strategy for better results.
What Are ERP Implementation Services?
ERP Implementation Services involve expert support that helps businesses plan, deploy, and integrate an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system into their existing operations. These services ensure that different departments such as finance, human resources, supply chain, manufacturing, and customer management work seamlessly within one unified platform, enhancing efficiency and data consistency across the organization.
ERP implementation services also include system customization, data migration, user training, and post-implementation support to ensure smooth adoption. The goal is to align the ERP solution with the company’s unique workflows and strategic goals. With the right implementation partner, businesses can minimize risks, reduce downtime, and achieve faster ROI from their ERP investment.
What Are the Core Elements of ERP Implementation Services?
Implementing an ERP system is a structured process that involves several critical stages. Each component contributes to ensuring the solution aligns with your business goals and delivers maximum efficiency. Here’s a closer look at the core elements that define effective ERP implementation services.

1. Needs Assessment & Planning
The first stage of ERP implementation involves analyzing the company’s overall objectives, existing processes, and operational challenges to identify areas that need improvement. During this phase, the organization evaluates its requirements and selects the most suitable ERP platform such as Microsoft Dynamics, SAP, or Oracle, based on functionality, scalability, and budget. A detailed roadmap is then developed to guide the entire implementation process, outlining timelines, resources, and key milestones.
2. System Design & Customization
In this stage, the ERP system is configured to align seamlessly with the company’s unique business workflows. The design process focuses on setting up modules and integrating functionalities that support core operations, ensuring smooth coordination between departments. Customization is carried out to tailor specific features according to the organization’s needs, making the system more efficient and user-friendly.
3. Data Migration
Data migration involves transferring essential information from legacy systems into the new ERP platform. This step ensures that historical and operational data are accurately moved without loss or duplication. Maintaining data accuracy, consistency, and security is a top priority throughout this process, as clean and reliable data form the foundation for effective decision-making and system performance.
4. Integration
In this phase, the ERP system is connected with existing business tools such as CRM software, e-commerce platforms, and other third-party applications. The goal is to ensure seamless communication and consistent data exchange across all departments. Effective integration allows real-time data sharing, enhances process visibility, and creates a unified digital ecosystem that supports better decision-making and operational efficiency.
5. Training & Change Management
Training and change management are essential to ensure employees can effectively use the new ERP system. Staff members are trained according to their specific roles and responsibilities so they can navigate the system confidently and perform daily tasks efficiently. Alongside technical training, change management focuses on guiding the organization through the transition, encouraging user adoption, and minimizing resistance to new processes or technologies.
6. Testing & Quality Assurance
Before the ERP system is fully implemented, thorough testing and quality assurance are carried out to verify that every component functions correctly. This involves unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing to detect and resolve technical issues or errors. Addressing these problems before deployment ensures the system operates smoothly and meets the organization’s performance and reliability standards.
7. Go-Live & Post-Implementation Support
The go-live stage marks the official launch of the ERP system for daily business operations. During this phase, the system is closely monitored to identify any issues that may arise and to ensure users can perform their tasks without disruption.
After deployment, continuous post-implementation support is provided, including system updates, maintenance, and performance improvements. This ongoing support helps maintain long-term system stability and ensures the ERP continues to meet evolving business needs.
“ERP implementation is not about installing software, it’s about changing the way people work.” – Rick Cook, ERP Industry Writer
What Are the Advantages of ERP Implementation Services?
ERP system implementation services provide numerous advantages that can greatly improve an organization’s operational efficiency, flexibility, and strategic decision-making. Below are some of the most impactful benefits they bring to businesses.
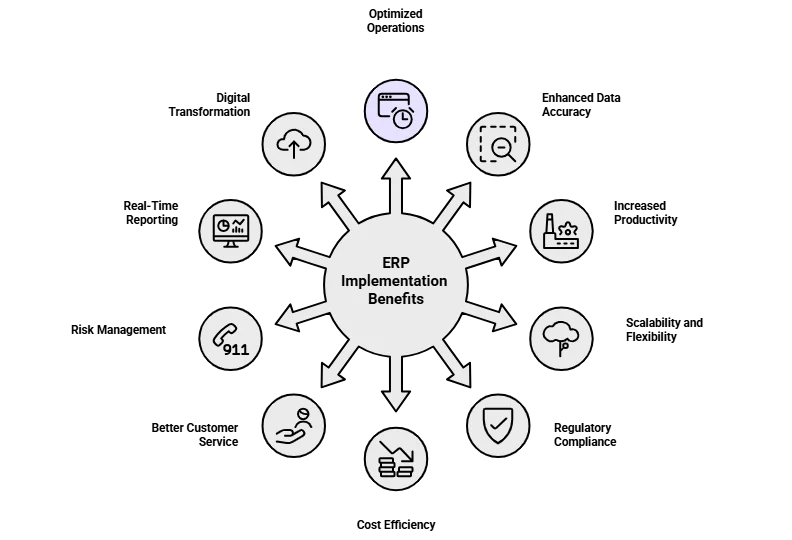
1. Optimized Business Operations
ERP implementation helps unify multiple departments such as finance, human resources, and supply chain into a single, cohesive system. By integrating these functions, businesses can eliminate repetitive manual tasks, reduce duplication of efforts, and streamline workflows. This not only improves operational efficiency but also fosters better collaboration and coordination across teams.
2. Enhanced Data Accuracy and Transparency
With centralized data storage, ERP systems ensure that information remains consistent, accurate, and easily accessible in real time. This unified data environment enhances visibility across the organization, enabling leaders to make quicker and more informed decisions. Additionally, advanced reporting and analytics tools within ERP systems provide valuable insights that support strategic planning and performance optimization.
3. Enhanced Productivity
ERP systems automate routine and time-consuming tasks, allowing employees to focus on more strategic and value-driven activities. With quicker access to accurate information, teams can respond faster to customer needs and operational challenges, improving overall efficiency and performance.
4. Scalability and Flexibility
A well-implemented ERP solution is designed to grow alongside your business. As your organization expands, you can easily add new modules, features, or users without disrupting existing operations. This adaptability ensures the system continues to meet evolving business requirements and supports long-term growth.
5. Regulatory Compliance
ERP systems come with built-in compliance tools that help organizations meet industry standards and adhere to legal regulations. They also simplify audit processes by maintaining clear and traceable documentation, ensuring transparency and accountability across all operations.
6. Cost Efficiency
By optimizing workflows and automating core business processes, ERP systems help reduce operational expenses and eliminate inefficiencies. Consolidating multiple systems into a single platform also minimizes IT maintenance costs, leading to long-term financial savings.
7. Better Customer Service
Integrated customer relationship management (CRM) capabilities within ERP systems enable businesses to manage customer data more effectively and enhance communication. Faster access to information and streamlined order processing result in quicker responses, improved service delivery, and stronger customer satisfaction.
8. Risk Management
ERP systems strengthen data security through advanced access controls and user permissions, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access or data breaches. Enhanced forecasting and planning capabilities also help organizations anticipate challenges, manage resources effectively, and minimize potential business risks.
9. Real-Time Reporting and Insights
With built-in dashboards and analytics tools, ERP systems deliver real-time, data-driven insights that support faster and more informed decision making. These features help track performance metrics, identify trends, and guide strategic planning to keep the business on the right path.
10. Support for Digital Transformation
ERP system implementation paves the way for adopting modern technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing. By integrating these innovations, businesses can modernize their operations, enhance efficiency, and stay competitive in an increasingly digital marketplace.
What are the Main Challenges for ERP Implementation Services?
While ERP implementation offers significant transformative advantages, it also presents several challenges that organizations need to address thoughtfully. Below is an overview of the most common ones:
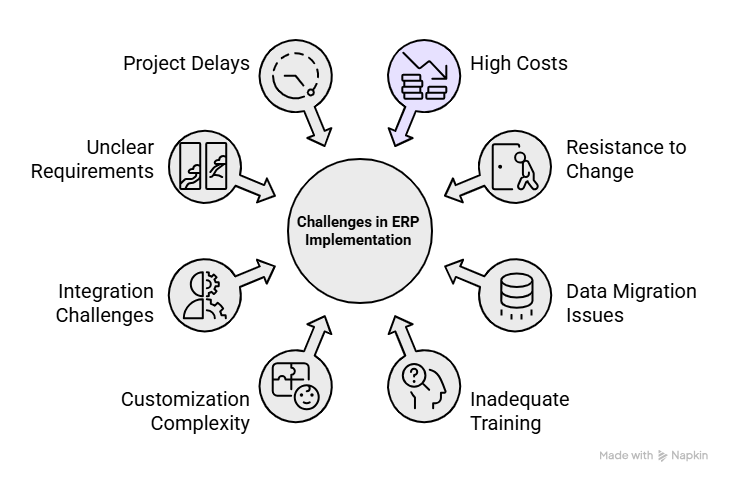
1. High Costs and Budget Overruns
Implementing an ERP system can be a costly endeavor, often exceeding the initial budget estimates. Factors such as scope expansion, system customization, and unforeseen technical complications tend to drive up expenses. Additionally, costs associated with software licensing, employee training, and external consulting services can accumulate rapidly, putting further pressure on the project budget.
2. Resistance to Change
Another significant challenge in ERP implementation is resistance from employees who may be hesitant to adapt to new technologies or altered workflows. Such reluctance can slow down adoption and reduce the effectiveness of the system. To address this, organizations must prioritize strong change management strategies and maintain clear, consistent communication throughout the transition process to ensure smoother acceptance and user engagement.
3. Data Migration Issues
Moving data from old legacy systems to a new ERP platform is often a complex and error-prone process. Inconsistent data formats, duplicate records, or poor data quality can lead to significant delays and inaccuracies during migration. Ensuring proper data cleansing and validation before the transfer is essential to maintain data integrity and avoid disruptions in operations.
4. Inadequate Training
A lack of comprehensive training can severely limit the effectiveness of an ERP system implementation. When users are not adequately trained, they may struggle to navigate the system or utilize its full capabilities, resulting in reduced productivity and low adoption rates. Providing hands-on, role-specific training ensures that employees can confidently use the system to its fullest potential and support overall operational efficiency.
5. Customization Complexity
While customization allows an ERP system to better fit an organization’s unique needs, excessive customization can create long-term challenges. Overly tailored systems can complicate future upgrades, increase maintenance requirements, and extend implementation timelines. Striking a balance between necessary customization and maintaining system flexibility is crucial for ensuring scalability and cost-effectiveness.
6. Integration Challenges
Integrating an ERP system with existing business applications such as CRM, e-commerce, or supply chain management tools can be technically complex. Compatibility issues, data synchronization problems, or lack of proper APIs can make the integration process difficult. When integration is not executed effectively, it can lead to data silos, inconsistent information flow, and workflow disruptions across departments. Ensuring a well-planned integration strategy and thorough testing is vital to maintain seamless connectivity and operational efficiency.
7. Unclear Requirements
One of the most common pitfalls in ERP implementation is the lack of clearly defined business requirements. When project objectives or functional needs are vague or frequently changing, it becomes challenging to design and configure the system appropriately. This often results in rework, confusion, and project misalignment. Establishing a clear project scope, along with detailed documentation and stakeholder alignment from the outset, is essential for a smooth and successful implementation.
8. Project Delays
ERP implementation projects are notorious for delays, often caused by underestimated system complexity, inadequate planning, or limited resources. When timelines extend beyond expectations, it can disrupt business operations and delay the realization of return on investment (ROI). To minimize such setbacks, organizations should adopt realistic timelines, allocate sufficient resources, and monitor progress closely through effective project management practices.
What are the Best Practices for ERP Implementation Services?
Achieving a successful ERP implementation demands strategic planning, strong teamwork, and the use of well-established methods. The following best practices can guide organizations in ensuring a seamless and efficient ERP deployment:
1. Define Clear Goals and Objectives
A successful ERP implementation begins with establishing clear and well-defined goals that align with the organization’s overall business strategy. Setting measurable key performance indicators (KPIs) allows teams to track progress and evaluate the effectiveness of the implementation. Having a clear direction helps ensure that the ERP system delivers tangible business value and supports long-term strategic objectives.
2. Secure Executive Sponsorship
Active involvement and support from senior leadership play a crucial role in the success of an ERP project. Executive sponsors help drive the initiative forward by ensuring proper resource allocation, addressing challenges, and promoting organization-wide commitment. Their backing also strengthens change management efforts, encouraging employees to embrace the new system and its processes.
3. Choose the Right ERP Solution
Selecting the appropriate ERP solution is fundamental to achieving a smooth and effective implementation. The chosen system should align with the company’s industry requirements, operational scale, and future growth ambitions. Organizations should also assess the software’s scalability, integration flexibility, and vendor reliability to ensure that the ERP system can adapt to evolving business needs over time.
4. Conduct Thorough Business Process Analysis
Before implementing an ERP system, it is essential to thoroughly analyze existing business processes to understand how operations currently function and where inefficiencies lie. Mapping current workflows helps identify areas for improvement, while designing optimized future-state processes ensures that the organization can fully leverage the ERP system’s capabilities. This approach not only streamlines operations but also aligns the technology with business goals for maximum effectiveness.
5. Plan for Change Management
Change management is a critical component of a successful ERP implementation. Organizations should clearly communicate the purpose, benefits, and expected impact of the new system to all stakeholders. Engaging employees early in the process helps reduce resistance and fosters a sense of ownership and collaboration. By addressing concerns proactively and promoting transparency, businesses can ensure smoother adoption and minimize disruptions during the transition.
6. Invest in Training and Education
Comprehensive training is vital to empower users and ensure effective use of the ERP system. Providing role-based training tailored to the specific responsibilities of each user group helps enhance confidence and competence. Combining hands-on practice sessions with user manuals, documentation, and e-learning tools allows employees to learn at their own pace and reinforces long-term system proficiency, leading to higher adoption rates and operational efficiency.
7. Ensure Data Quality and Governance
Maintaining high data quality is crucial for the success of any ERP system implementation. Before migrating data from legacy systems, organizations should focus on cleansing, validating, and standardizing information to eliminate duplicates, errors, or outdated entries. Establishing clear data ownership and governance protocols ensures ongoing accuracy and accountability, allowing the ERP system to deliver reliable insights and support informed decision-making.
8. Avoid Over-Customization
While customization can help tailor an ERP system to meet specific business needs, excessive modifications often create long-term complications. Over-customizing the system can make future upgrades more difficult, increase maintenance costs, and extend implementation timelines. To prevent these issues, organizations should rely on standard ERP features whenever possible and reserve customization for truly strategic needs. Any custom changes should be carefully planned, documented, and aligned with overall business objectives to maintain system flexibility and sustainability.
How to implement an ERP system?
Implementing an ERP system is a detailed yet highly beneficial process that brings together multiple business operations within a single, cohesive platform. The following step-by-step guide outlines the key stages to help you plan and execute a successful implementation:
1. Define Objectives and Scope
The first step in ERP implementation is to clearly define the objectives and scope of the project. Begin by identifying the specific business challenges the ERP system is expected to address whether that’s improving efficiency, enhancing data accuracy, or enabling scalability. Establish measurable goals that align with the organization’s strategic vision. It’s also important to determine the scope of implementation by identifying which departments and functions, such as finance, human resources, or inventory management, will be included in the initial rollout.
2. Assemble a Project Team
A dedicated project team is essential to ensure a smooth and coordinated ERP implementation. This team should include stakeholders from all key departments to represent diverse operational needs and perspectives. Clearly assign roles such as project manager, IT lead, and departmental heads to oversee different aspects of the process. Additionally, securing executive sponsorship provides the necessary support, authority, and resources to drive the project successfully.
3. Choose the Right ERP System
Selecting the appropriate ERP system is a critical decision that influences the success of the entire implementation. Organizations should evaluate potential vendors based on their compatibility with the industry, the range of features and modules offered, and the system’s ability to integrate with existing software.
Customization options, total cost, and the level of vendor support should also be carefully assessed to ensure the chosen solution meets both current requirements and future growth plans. Examples include ERP solutions such as Microsoft Dynamics 365, SAP, Oracle, and NetSuite.
4. Plan the Implementation
Developing a comprehensive implementation plan is a key step in ensuring the ERP project runs smoothly. This plan should outline the overall timeline, key milestones, and budget allocations for each phase of the project. Another important decision involves choosing the deployment approach, whether to host the ERP system on-premise or in the cloud, and determining the rollout strategy, such as a phased implementation or a full-scale launch. A well-structured plan helps maintain control over resources, schedules, and project deliverables.
5. Data Migration
Data migration is one of the most crucial and sensitive stages of ERP system implementation. It begins with auditing existing data to verify its accuracy, completeness, and relevance. Once reviewed, the data must be cleaned, standardized, and mapped appropriately to align with the new ERP system’s fields and structure. Conducting test migrations with sample data helps identify and fix potential issues early, reducing the risk of errors during the final transfer.
6. System Configuration and Customization
After data preparation, the ERP system should be configured to align with the organization’s specific business processes. Each module, such as finance, HR, or supply chain, must be tailored to operational needs while maintaining consistency across departments.
Customization should be kept minimal and strategic to prevent future maintenance challenges and unnecessary complexity. Additionally, setting up appropriate user roles and permissions ensures data security and controlled system access across different levels of the organization.
7. Testing
Before the ERP system is officially launched, thorough testing is essential to ensure that all components function correctly and align with business requirements. This includes conducting unit testing, integration testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT) to evaluate both individual modules and their interaction across the system. Simulating real-world scenarios helps identify bugs or process gaps, allowing the team to make necessary adjustments and refine workflows before the system goes live.
8. Training and Change Management
Comprehensive user training and strong change management are critical for successful ERP adoption. Training should be tailored to each user’s role, ensuring that employees understand how to use the system effectively in their daily tasks. Providing user manuals, interactive workshops, and continuous support helps build confidence and competence. At the same time, clear communication about the benefits of the ERP system fosters positive engagement and reduces resistance to change.
9. Go Live
The go-live phase marks the transition from planning to full-scale operation. Organizations must choose an appropriate go-live strategy, whether phased, parallel, or full deployment, depending on their readiness and risk tolerance. Continuous monitoring of system performance and user feedback during this period is vital to quickly identify and address issues. Having technical support readily available ensures a smooth transition and minimizes operational disruptions.
10. Post-Implementation Support and Optimization
After the system is live, ongoing support and optimization are essential to maintain long-term success. Regular reviews of system performance help identify areas for improvement and ensure the ERP continues to meet evolving business needs.
Organizations should also look for opportunities to optimize workflows and introduce new features when it is beneficial. Maintaining a strong relationship with the ERP vendor ensures timely updates, security patches, and technical assistance, keeping the system efficient and up to date.
Seamless ERP Implementation with Intelegain
Now that you have a clear understanding of the ERP implementation process, it is the right time to take the next step. For a reliable platform and exceptional implementation support, connect with intelegain for comprehensive ERP solutions. Intelegain helps businesses implement and customize Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, one of the most trusted and intelligent ERP solutions available today.
Business Central empowers organizations with real-time insights, seamless process automation, and a unified platform that connects all core operations. With its flexibility, scalability, and user-friendly interface, it enables businesses to enhance efficiency, strengthen collaboration, and adapt quickly to changing market needs.
FAQs
A business should choose an ERP partner with strong industry experience, deep technical knowledge, and a clear understanding of its operational goals.
ERP implementation delivers measurable ROI through improved operational efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced data visibility, and faster, more informed decision-making.
The key stages of ERP implementation include planning, selecting the right software, configuring the system, migrating data, conducting thorough testing, training users, and finally, going live with the solution.
The main ERP implementation methodologies include Big Bang, Phased Rollout, Parallel Adoption, Pilot Implementation, and Hybrid, each offering a unique approach to deploying the system based on an organization’s size, complexity, and risk tolerance.
An ERP implementation consultant brings technical expertise and industry insights, helping avoid common pitfalls, ensure timely execution, and achieve a successful ERP rollout.
Let’s Discuss Your ERP Implementation Strategy