As artificial intelligence moves from the experimental phase to everyday use, an important difference is emerging between agentic ai vs generative ai.
Both represent major breakthroughs, but they’re designed for different purposes. Generative AI is in the spotlight for its ability to create original text, images, and even music. Meanwhile, Agentic AI is transforming autonomy in business operations, allowing systems to make decisions, adapt to change, and carry out complex tasks with little human oversight.
Over 78% of companies now use Generative AI in at least one business function and nearly 30% report deploying Agentic AI, highlighting the growing importance of both capabilities. For businesses aiming to innovate, automate processes, and work smarter, understanding the strengths and limitations of each AI type is no longer optional.
As Alphabet CEO Sundar Pichai has stated, “AI is probably the most important thing humanity has ever worked on.”
In this article, we’ll explain the core differences between Generative AI and Agentic AI, explore examples of each, and help you determine which approach best fits your needs.
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI is a type of artificial intelligence built to work independently, capable of pursuing set goals and making decisions without constant human input. Unlike traditional AI, which typically follows fixed rules or predefined responses, Agentic AI takes a proactive approach, adapting to new situations, modifying its strategies to achieve objectives, and learning continuously from real-world experiences.
With these abilities, Agentic AI services functions as an autonomous agent, managing complex tasks while steadily enhancing its performance over time. Many companies now leverage AI and ML services to automate processes, gain insights from data, and improve decision-making across various industries.
Key Features of Agentic AI
Agentic AI stands out because of its ability to work independently, adapt to change, and learn from experience. The following key features highlight what makes it different from traditional AI systems.
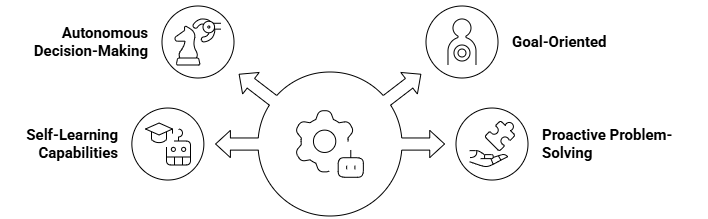
1. Autonomous Decision-Making
Agentic AI can make decisions on its own without human intervention. Using agentic automation, it processes data, evaluates potential risks, and determines the most effective course of action to achieve its goals.
2. Goal-Oriented
Rather than relying on fixed, pre-programmed rules, Agentic AI works toward defined goals. It breaks these goals into actionable steps, prioritizes tasks, and adapts dynamically to remain aligned with desired outcomes.
3. Self-Learning Capabilities
Agentic AI improves its performance over time by learning from real-world interactions and the results of its actions. It updates its strategies based on new data, feedback, and environmental changes, enabling it to tackle increasingly complex tasks more efficiently.
4. Proactive Problem-Solving
Instead of waiting for instructions, Agentic AI anticipates challenges, analyzes situations, and initiates solutions to keep moving toward its objectives.
Examples of Agentic AI
Generative AI has become widely recognized for its ability to create original and high-quality content across various formats. From text and images to music and code, its applications span numerous industries. Below are some notable examples of Generative AI in action.
1. Autonomous Agents
These systems, similar to virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa, go beyond simply responding to commands. They anticipate needs, make decisions, and take action based on your requests without the need for continuous guidance. As of 2025, over 8.4 billion voice assistants are in use worldwide, surpassing the global human population.
2. Robotics
In fields like healthcare and manufacturing, agentic AI-powered robots are transforming operations. Just like surgical robots that can assist doctors in complex procedures or factory robots that can adapt their assembly process to product variations, they adjust their actions in real time to complete tasks efficiently. Robotic systems like the da Vinci Surgical System facilitated approximately 2.63 million surgical procedures in the U.S. last year, marking a 17% increase from the previous year. Globally, these systems have performed more than 14 million procedures overall.
3. Self-Driving Cars
Similar to how autonomous vehicles like those from Tesla or Waymo operate, agentic AI enables cars to navigate roads without human input. They make split-second decisions such as when to accelerate, brake, or change lanes, based on live data about traffic, road signs, and obstacles. Waymo currently provides over 250,000 paid robotaxi rides per week across several U.S. cities. Tesla has launched a small robotaxi pilot in Austin with about 10 to 12 vehicles, offering rides at a flat rate of $4.20, though a safety operator still rides onboard.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI is a branch of artificial intelligence that specializes in producing new content like text, images, audio, video, or code by recognizing patterns and structures within large datasets. These systems leverage machine learning techniques, particularly deep learning and neural networks, to study existing data and create original results based on user inputs. By mimicking human creativity, Generative AI is revolutionizing how content is created, making it possible to automate complex creative tasks and unlock new opportunities across various fields.
Key Features of Generative AI
Generative AI is transforming how we create and interact with digital content. Understanding its core features helps reveal why it’s such a powerful tool across industries and applications.
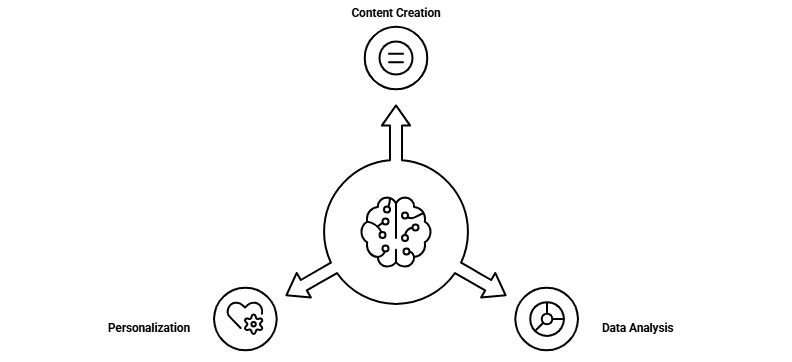
1. Content creation
Generative AI excels at producing original material across various forms like text, images, audio, and video. Using deep learning models, it interprets prompts to generate coherent outputs that mimic human creativity on a broad scale.
2. Data analysis
In addition to generating content, Generative AI can analyze extensive datasets to identify patterns, extract valuable insights, and produce concise summaries. This helps speed up decision-making by turning complex data into clear, actionable information.
3. Personalization
Generative AI customizes content, recommendations, and interactions based on individual user preferences and behaviors. It adjusts its outputs to suit specific needs, delivering more engaging and personalized experiences across different platforms.
Examples of Generative AI
Generative AI is already making a significant impact across various fields by creating original content and solutions. The following examples showcase how this technology is being applied in real-world scenarios.
1. Generative Content Creation
Generative AI is highly proficient at producing clear and contextually appropriate content. For instance, OpenAI’s ChatGPT can craft essays, respond to queries, and build conversational agents based on user prompts. Approximately 83% of content creators incorporate AI into their workflows, with 38.7% using AI throughout their entire process and 44.2% utilizing it in parts of their workflow.
2. Product Design and Development
Across product teams, AI design tools powered by generative AI spark innovation by producing design concepts, prototypes, and user-centric feature ideas. They enable faster iterations, broader exploration, and improved efficiency throughout the development process. For example, Figma’s AI-powered plugin, which helps designers generate layouts and ideas, has seen a 30% increase in team productivity since its launch.
3. Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
Generative AI enhances chatbots and virtual assistants by enabling them to hold more natural, dynamic conversations. These systems can better understand user intent, craft human-like responses, and address a wider variety of customer queries without relying solely on scripted replies. For example IBM Watson Assistant, which integrates generative AI to improve response accuracy and user satisfaction, contributing to a reported 30% increase in first-contact resolution rates for companies adopting the platform.
Key Differences Between Agentic AI vs Generative AI
When comparing agentic AI vs generative AI, one must consider that generative AI relies on user prompts, whereas agentic AI operates independently to achieve set goals. While both Generative AI and Agentic AI are advancing the capabilities of artificial intelligence, they serve distinct roles and functions. Understanding their key differences is essential to grasp how each impacts technology and business applications.
| Aspect | Generative AI | Agentic AI |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | AI that creates original content like text, images, music, or videos, focusing on delivering imaginative and creative results. | AI that performs goal-driven tasks, makes autonomous decisions, and adapts to dynamic environments. |
| Core Functionality | Leverages extensive datasets to identify patterns and generate new, original content inspired by those patterns. | Assesses the environment, takes decisions, and modifies actions to accomplish goals. It aims to carry out tasks in an efficient manner. |
| Interaction Style | Typically cooperative, functioning by responding to prompts, instructions, and input provided by users to create content. | Completely independent; after initial setup, it operates on its own without requiring ongoing human interaction. |
| Technologies Used | Utilizes Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Transformer models such as GPT and BERT to create content. | It employs reinforcement learning, decision trees, robotics frameworks, and sensor fusion to engage with its environment and execute tasks. |
| Strengths | Highly skilled in creativity, automating content creation, and boosting human innovation by generating extensive amounts of material. | Recognized for its efficiency, independence, and capacity to operate at scale within complex, ever-changing environments that demand decision-making. |
Future of Agentic AI vs Generative AI
As generative and agentic AI continue to advance, the distinction between them is likely to become less clear. One significant contrast in the agentic AI vs generative AI discussion is that agentic AI adapts and learns from experience, while generative AI excels at producing original content from learned pattern Future technological progress may produce systems that seamlessly blend creativity with autonomous action, combining the strengths of both approaches. Imagine an AI that not only creates original ideas but also carries them out on its own, which has the potential to transform industries such as healthcare and manufacturing.
At the same time, this great potential brings a shared responsibility. It is essential to develop and use these technologies ethically while ensuring transparency and accountability. By understanding the differences between generative and agentic AI, we can better appreciate their unique capabilities and work toward a future where AI creates meaningful and positive impacts for humanity. If you want to learn more or explore how these AI advancements can benefit your business, reach out to us today.
FAQs
A great example of agentic AI in action is FedEx, which leverages this technology for supply chain optimization. The company benefits from AI’s intelligent logistics management, allowing it to efficiently manage routes and inventory levels with minimal human intervention.
Understanding the differences helps organizations choose the right AI technology for their needs, whether they require creative content generation or autonomous decision-making and action.
Agentic AI benefits businesses by autonomously making decisions and executing complex tasks, which improves efficiency, reduces human error, and enables scalable operations in dynamic environments.
Generative AI is best suited for creative work like writing, designing, and multimedia production, whereas agentic AI is focused on autonomous execution of complex tasks and decision-making.